About us

We are a consortium of 14 partners composed of seven research organizations, four small and medium enterprises, one large company, and two user associations engaged in the design of Trustworthy AI methods and tools for automated vehicles.
1 — Overview
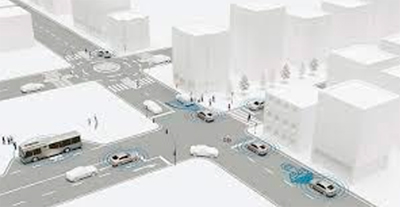
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is considered one of the key enabling technologies that can lead to the successful deployment of connected and automated vehicles (CAVs). By taking advantage of the huge amount of sensor data and supporting all aspects of the sense-plan-act paradigm, AI can revolutionize the future of automotive mobility services. However, the benefits of AI in CAVs are hampered by ethical risks that can compromise its adoption by vulnerable road users (VRUs) such as pedestrians, cyclists, or persons with disabilities. Developed at the European level, the ethical guidelines of Trustworthy AI advocate the development of transparent, responsible, and human-centric AI systems and the ethical recommendations for CAVs suggest reducing opacity in algorithmic decisions by developing “explainability-enhancing technologies in relation to data collection and algorithms used for CAV decision-making”.
Considering Artificial Intelligence (AI) capabilities and potential risks, and taking into account its limitations, AI4CCAM will develop an open environment for integrating trustworthy-by-design AI models of vulnerable road user behavior anticipation in urban traffic conditions, and accounting for improved road safety and user acceptance. Leveraging the Trustworthy AI guidelines for general intelligent software systems and the ethical recommendations for connected automated vehicles, AI4CCAM will support AI-based scenarios management in which pedestrian/cyclist behavior anticipation models will integrate visual gaze estimation and where explainable ego car trajectory prediction models are simulated with ethical dilemmas and multiplied with generative adversarial networks and metamorphic testing techniques.
2 — Objectives
AI4CCAM aims at developing an open environment for Trustworthy AI in CCAM operations, including:
- Simulated and synthetic urban-traffic scenarios involving VRUs and an interoperable digital framework to manage and multiply these scenarios in conformance with Trustworthy AI requirements and security measures
- Documentation about the risks related to the usage of AI in CAVs, an online participatory space for assessing and fostering the adoption of Trustworthy AI in CCAM
- Simulated scenarios exhibiting human-vehicle AI-based interactions and ethical dilemmas, advanced AI models for CCAM situation awareness and VRUs behavior anticipation, and car trajectory prediction.

The ultimate impact goal of AI4CCAM is to foster the adoption of Trustworthy AI in CCAM to support the European strategy for green, smart and affordable mobility by contributing to innovation and the use of data and artificial intelligence. To achieve this goal, the project will pursue five specific objectives:
- Develop an interoperable digital framework for Trustworthy AI in CCAM for managing and generating urban-traffic simulation scenarios
- Define Trustworthy AI for CCAM: Ethical, Social and Cultural Implication (ESC) and improve CAV user acceptance using biased-free datasets
- Define use cases exhibiting human-vehicle AI-based interactions and ethical issues with impact assessment
- Design trustworthy-by-design AI models for CCAM situation recognition and robust action forecast
- Boost outreach and dissemination activities, and set the basis for further developments, sustainability, and replication of the project results
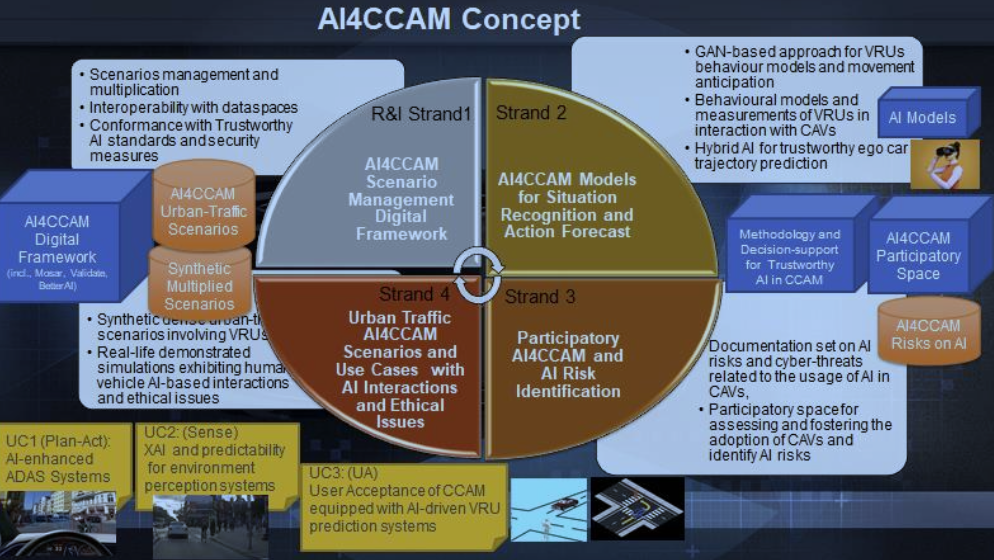
3 — Concept and Methodology
In order to fulfil its ambitions, AI4CCAM is driven by a concept and methodology which aims to address the following high-level challenges:
- Challenge related to urban-traffic scenarios management and generation. The interaction between Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) and automated vehicles is not yet sufficiently explored, especially for the Plan and Act operations of the Sense-Plan-Act paradigm. Indeed, i) existing scenarios are currently limited to the interaction with a single VRU while realistic scenarios shall involve multiple VRUs, ii) urban traffic scenarios do not involve AI-based dialogue interaction between the automated vehicle and VRUs, iii) the generation of systematic (synthetic) AI-based scenarios involving ethical dilemmas and social impact is currently insufficient.
- Challenge related to Machine Learning model robustness. Even though the usage of Deep Learning is dominant in the Sense part, the deployment of AI in real-time Plan-Act remains difficult and under-explored because of lack of robustness, explainability, safety and security. Also, used datasets for model training are verified for checking the absence of biases and augmented to improve the robustness of models.
- Challenge related to the design of trustworthy-by-design AI decision-making and action explanation. Current DL models, trained with multiple advanced datasets, are opaque and embed only little explanation means. The level of user interpretation and understanding of decisions taken by CAVs (data scientists, car manufacturers, passengers, VRUs, road regulators) is still too low. Also, ethical dilemmas and AI risks are not yet sufficiently tested in simulations.
- Challenge related to user acceptance of CAVs. User acceptance of AI-based behaviour anticipation and car trajectory prediction is not sufficiently explored, especially when multiple VRUs are involved. AI cyber-threats is also a concern for many informed road users and authorities. SSH studies are required to better understand how to remedy such challenge.
4 — Working Plan
The project has a duration of 36 months (from January 2023 to December 2025) and includes the Work Packages (WPs):
WP1
AI-based integrated Trustworthy AI framework for CCAM
Provide a methodology assisting stakeholders in the adoption of Trustworthy AI in CCAM; provide a data-driven trustworthy environment to develop and validate trustworthy AI; provide value-oriented analysis of data sources and data models accommodating provisions.
WP2
Advance AI-driving CCAM sense-plan-act predictive models
Design novel AI and experiment based VRU behavioral models and movement anticipation; design trustworthy AI ego car trajectory prediction models in urban traffic scenarios involving VRUs; situation risk estimation.
WP3
Trustworthy AI for CCAM: Ethical, Social and Cultural Implication (ESC)
Define a trustworthy documentation framework for CCAM to implement responsible practices and accountability, taking into account risks and ethical/moral dilemmas related to AI decision making raise awareness to CCAM stakeholders of ELSEC (Ethical, Legal, Societal, Economic and Cultural) requirements; identify and understand the different biases that impact of Trustworthy AI based CCAM amongst users and VRUs; develop a human-centric framework for the conception of AI-based CCAM to increase user acceptance from an early stage; create a space for cooperative learning, reflection and discussion; understand the perceptions of Trustworthy AI in CCAM; create a long-term Ethical Advisory Board that will assess the usage of AI in CCAM.
WP4
Use Case Implementation and Validation
Define a validation process that embraces the variety of CCAM Use Cases involving explainability and Trustworthy AI concepts; evaluate AI4CCAM digital framework and AI models in dedicated Use Cases representing real life CCAM scenarios and collect all necessary evidence for validation; perform impact assessment in line with the use case scenarios.
WP5
Communication, Dissemination and Exploitation for the AI and CCAM ecosystems
Implement a well-focused dissemination and communication plan ensuring high-quality content distributed through relevant dissemination channels, and coordinate stakeholder engagement activities.
WP6
Project coordination and management
Provide the needed framework to enable the project to achieve its objectives while meeting its cost, time, and quality requirements. This includes the administrative, financial, and legal management.